Research: Q3 US digital health funding hits $2.4B across 110 deals
The digital health landscape in the U.S. in Q3 2024 showed a shift towards more focused and strategic growth. Although the number of deals has decreased, the sector remains active — with investors making fewer but more calculated investments. Companies continue to launch new products and form partnerships, with many focusing on building stronger positions in the market to compete against legacy healthcare providers.
In addition to strategic investment, mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are becoming more prevalent, as digital health players weave together new features and capabilities to strengthen their offerings.
Key takeaways
Here's what you should know:
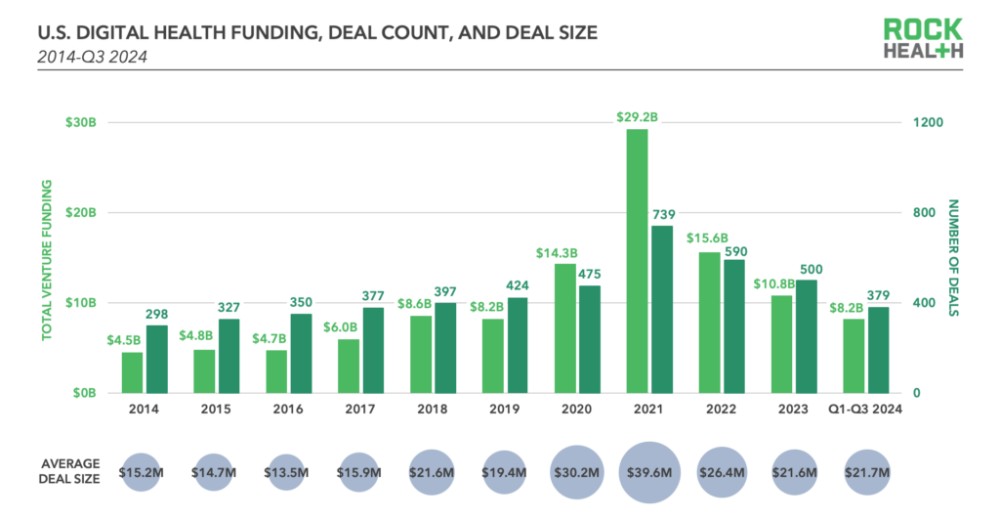
- Investment trends: In Q3 2024, the digital health sector saw $2.4 billion in venture funding across 110 deals, bringing the year-to-date total to $8.2 billion. While the number of deals dropped from previous quarters (136 in Q1, 133 in Q2), the average deal size remained stable at $22 million. This consistency signals that investors are being selective, making fewer but more strategic investments. The funding is also being funneled into companies that investors have already vetted, suggesting stronger confidence in these partnerships, especially in areas like healthcare AI.
- Partnerships and strategic collaborations: Some companies are forming deeper partnerships, often between digital health and tech companies, to drive innovation. One example is Hippocratic AI, which received $17 million from Nvidia's venture arm after a previous collaboration to develop healthcare-focused language models. This shows how tech companies are playing an increasingly crucial role in digital health innovation through both funding and technological support.
- IPO recalibration and public market pressures: Companies like R1 RCM and 23andMe have been reassessing their positions in the public markets, with some opting to go private. This recalibration comes in response to the increasing regulatory and financial pressures of being publicly traded. The case of Nuvo, which declared bankruptcy just months after going public via a special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC), underscores the risks of entering public markets prematurely.
- Mergers and acquisitions (M&A): Q3 2024 saw a decrease in M&A activity, logging just 21 deals compared to the quarterly average of 37 in 2023. However, the nature of these deals is shifting. Rather than acquiring direct competitors, companies are focusing on so-called "tapestry acquisitions" — purchasing businesses that add new features and capabilities to their existing platforms. This allows companies to scale quickly and offer a more comprehensive set of solutions to customers. Notable examples include DarioHealth acquiring Twill to enhance its mental health offerings and Commure's acquisition spree to build out its provider operating system.
- Profitability and sustainability: The decision to "buy versus build" is becoming a more attractive option for digital health companies looking to expand without overextending their resources. By acquiring established products and features, companies like Fabric Health and DarioHealth are broadening their offerings and accelerating their paths to profitability. This shift toward sustainable growth reflects a more mature approach in the sector, where companies aim to be fiscally responsible while still scaling their operations.
These key takeaways reflect the ongoing transformation in the digital health sector, where companies are balancing innovation with discipline, strategic partnerships, and focused investments to maintain their market position and grow sustainably.
Why does it matter?
The developments in Q3 2024 reveal the maturing strategies within the digital health sector in the U.S.. Companies are no longer seeking to grow by sheer volume of activity but rather through well-considered moves that enhance their long-term sustainability and market positioning. By weaving new features and capabilities into existing offerings through acquisitions, companies are addressing a wider range of consumer needs. This more nuanced approach to growth underscores the importance of integrating innovations to remain competitive in a crowded marketplace.
As one CEO mentioned, "The decision to build versus buy was straightforward for us. Given the capital requirement and the time it takes to build, the buy option was much more attractive."
This sentiment reflects how companies today are balancing growth with fiscal responsibility.
The context
In the broader context of digital health, 2024 has been a year of recalibration. The high deal activity that characterized previous years has given way to a more strategic approach. The focus now is not just on funding, but on how digital health players can integrate new technologies and features into their existing platforms to compete more effectively against traditional healthcare providers.
The mentioned trend of "tapestry acquisitions" is all about that, with companies acquiring others not to eliminate competition but to strengthen their offerings. These acquisitions allow companies to scale efficiently, providing more comprehensive services to their clients. As illustrated by DarioHealth's acquisition of Twill to expand into mental health, this strategy helps digital health players grow in a way that is both cost-effective and beneficial for customers.
In short, the digital health market is evolving from single-solution companies toward combined offerings that can meet broader healthcare needs — a shift that will likely continue to define the sector moving forward.
💡Did you know?
You can take your DHArab experience to the next level with our Premium Membership.👉 Click here to learn more
🛠️Featured tool
 Easy-Peasy
Easy-Peasy
An all-in-one AI tool offering the ability to build no-code AI Bots, create articles & social media posts, convert text into natural speech in 40+ languages, create and edit images, generate videos, and more.
👉 Click here to learn more


