Lunit, AstraZeneca working together on AI-powered digital pathology risk assessment tools for NSCLC
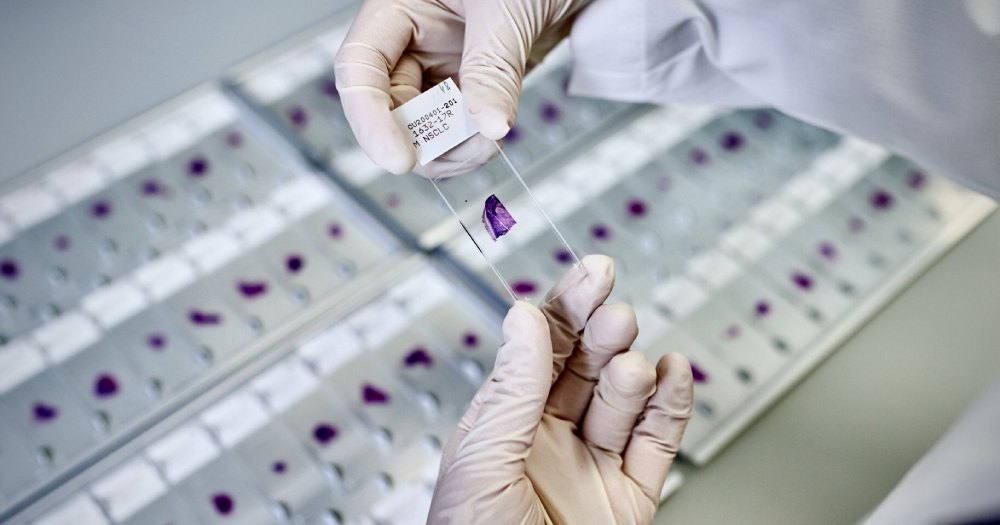
Leader in AI-driven cancer diagnostics Lunit has partnered with pharmaceutical giant AstraZeneca to revolutionize lung cancer treatment. Their collaboration focuses on the development of Lunit SCOPE Genotype Predictor, an innovative AI tool designed to assess risk and predict driver mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
This advancement promises faster and more cost-effective solutions for precision oncology, particularly in identifying genomic alterations such as Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) mutations.
How does it work?
The Lunit SCOPE Genotype Predictor employs cutting-edge deep learning algorithms to analyze hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) slide images-standard pathology samples stained with hematoxylin and eosin. By examining these slides, the AI estimates the likelihood of genomic alterations like epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations that drive NSCLC.
This predictive insight is delivered before the results of traditional molecular tests, allowing medical practitioners to prioritize samples for further testing. This approach streamlines diagnostics, saving critical time and resources.
As Brandon Suh, CEO of Lunit, explains, "The integration of this tool as a screening test into pathology workflows promises to improve the opportunity for patients to benefit from appropriate targeted therapy."
Why does it matter?
Traditional genomic testing for NSCLC is often delayed due to its complexity and cost, leading to treatment decisions based on incomplete information. This urgency is a significant barrier to effective cancer care. By introducing a rapid and reliable AI screening method, Lunit and AstraZeneca aim to bridge this gap.
The potential impact on patient outcomes is immense. Kristina Rodnikova, Head of Global Oncology Diagnostics at AstraZeneca, emphasizes the importance of tools like this, stating, "This collaboration underscores our commitment to advancing precision medicine in oncology. These tools will help address unmet needs by optimizing diagnostic workflows for NSCLC patients."
The context
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging cancers to diagnose and treat, with NSCLC making up the majority of cases. Driver mutations like EGFR play a crucial role in determining effective therapies, yet genomic testing often falls short due to logistical challenges. This collaboration seeks to validate Lunit's AI tool in real-world settings, ultimately making these solutions accessible to labs and healthcare facilities globally.
Beyond NSCLC, the partnership aims to extend the AI's capabilities to predict other molecular biomarkers, further advancing precision oncology. By enabling healthcare providers to quickly identify actionable insights, this initiative could mark a turning point in cancer diagnostics and treatment planning.
💡Did you know?
You can take your DHArab experience to the next level with our Premium Membership.👉 Click here to learn more
🛠️Featured tool
 Easy-Peasy
Easy-Peasy
An all-in-one AI tool offering the ability to build no-code AI Bots, create articles & social media posts, convert text into natural speech in 40+ languages, create and edit images, generate videos, and more.
👉 Click here to learn more


