An eye scan can detect signs of Parkinson’s seven years before diagnosis
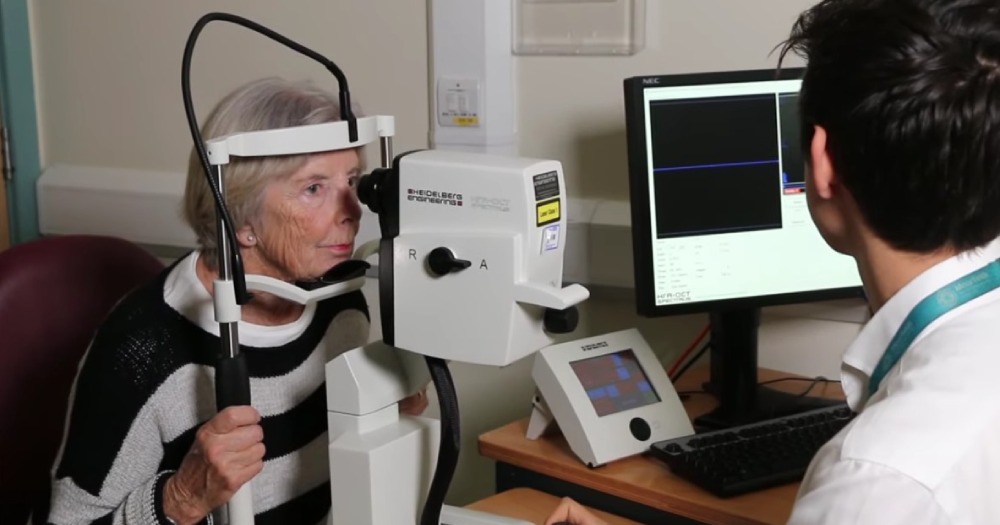
Researchers from Moorfields Eye Hospital and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology have discovered eye markers that can indicate Parkinson's disease up to seven years before clinical symptoms appear.
This groundbreaking finding was made possible by analyzing the largest retinal imaging study on Parkinson's disease using AI and two extensive datasets, AlzEye and UK Biobank.
The study, published in the medical journal Neurology, is part of an emerging field of research called "oculomics," which leverages high-resolution images of the retina and AI to uncover hidden information about neurodegenerative conditions and other diseases from eye scans.
Highlights
- Early detection: The study demonstrates the potential of using eye data and AI technology to detect very early signs of Parkinson's disease, opening up new possibilities for treatment and prevention.
- Largest study and datasets: The study is the largest of its kind to date on retinal imaging in Parkinson's disease, and the findings were replicated using two large and powerful datasets, AlzEye and UK Biobank, despite the relatively low prevalence of Parkinson's disease.
- Non-intrusive method: The retina is the only place in the body where a non-intrusive view of cell layers below the skin's surface can be obtained. This makes the use of OCT scans a precious tool for detecting signs of various diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders, without invasive procedures.
- Potential for pre-screening tool: Although the method is not yet ready to predict whether an individual will develop Parkinson's, the researchers hope it could soon become a pre-screening tool for people at risk of the disease.
Why does it matter?
Early detection of Parkinson's disease can lead to timely interventions, lifestyle changes, and potentially delay the onset and impact of this life-changing neurodegenerative disorder.
The use of non-invasive, lower-cost, and quicker OCT scans for predictive analysis can have a significant impact on public health by enabling pre-screening of at-risk populations and ultimately preventing some conditions from arising.
The study highlights the potential of oculomics and AI in revolutionizing the way we detect and manage neurodegenerative diseases and other health conditions.
💡Did you know?
You can take your DHArab experience to the next level with our Premium Membership.👉 Click here to learn more
🛠️Featured tool
 Easy-Peasy
Easy-Peasy
An all-in-one AI tool offering the ability to build no-code AI Bots, create articles & social media posts, convert text into natural speech in 40+ languages, create and edit images, generate videos, and more.
👉 Click here to learn more


